What Is a Drain Interceptor & What Are They Used For?
A drain interceptor, also known as a fuel interceptor, petrol interceptor, or oil interceptor, is a defensive device that separates and captures contaminants before they reach a drainage system. Commonly used in industrial or commercial settings such as petrol stations or car parks, the device captures waste like oil or petrochemicals spilled onto the ground by vehicles, preventing contaminants from flowing into main surface water sewers. This can occur during rainfall or when washing vehicles. These types of interceptors can also be found at production or manufacturing sites and storage facilities. Fats, Oils and Grease (FOG) can also be captured by a grease interceptor, which works similarly to a petrol interceptor.
The drain interceptor definition can sometimes be confused with older Victorian-era interceptor drain traps, which were originally used to prevent the spread of airborne diseases, block rodents and reduce sewer odours.
What Is the Purpose of an Interceptor?
The purpose of a drain interceptor is to ensure that contaminants do not flow into the main surface water sewers, safeguarding drainage systems and the environment by preventing harmful substances like oil, petrol, and other pollutants from entering water sources. They are vital in wastewater management systems as they play a huge part in protecting the environment. Environmental authorities can request drain interceptors to be placed in high-risk areas where the likeliness of contamination is greater.
How Does a Drain Interceptor Work?
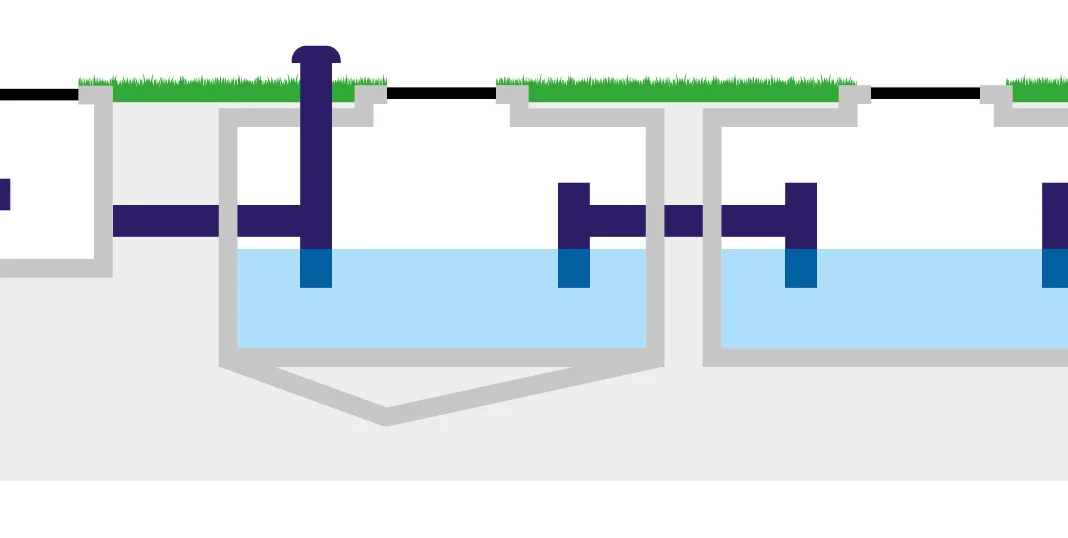
Drain interceptors work by using a multi-chambered design to effectively separate contaminants from surface water before it reaches the main sewer system. The surface water from roads and car parks flows into the first chamber, which is vented to remove odours and gases safely. On entering the chamber, the speed slows, allowing heavier solids like dirt and sediment to settle at the bottom while lighter oils and petrol rise to the top due to their lower density.
Each subsequent chamber further refines this separation, ensuring that most pollutants are trapped. The interceptor’s design minimises turbulence, preventing contaminants from mixing back into the water, and uses baffles to guide flow and enhance separation. Clean water stays in the middle and can exit the interceptor on its way to the sewer system or a designated outlet.
Any contaminants that have been captured are removed from the interceptor drain using methods including pumping, skimming, or manual cleaning depending on tank size.
What Is the Difference Between a Separator and an Interceptor?
While both the terms “separator” and “interceptor” are used in fluid management, there is a key difference. A separator typically refers to a device that actively separates mixtures into their individual components based on physical properties, such as density. An interceptor, on the other hand, serves a more specific purpose. It is designed to capture and prevent pollutants, such as oil or grease, from entering the drainage system. Essentially, an interceptor can be considered a type of separator with a targeted role, focusing on blocking harmful contaminants to protect water quality and ensure compliance with environmental standards.

Talk to your local Metro Rod specialist
We are always happy to arrange a free site assessment and no obligation quotations for any work you might need. Alternatively, you can call our emergency hotline number on 0800 66 88 00
Get in touch Drainage Services

